Difference between revisions of "Grism"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
On the left, a 140 mm focal length negative achromat collimates the beam from the CDK telescope before it reaches the focal plane. At f/6.8 the beam for a point source on axis is 20.5 mm in diameter at this lens. Immediately after the lens the beam enters an anti-reflection coated wedge prism that deflects it 6 degrees off axis. This approximately compensates for the diffraction angle of a 150 groove/mm grating blazed at 580 nm that is close to the second prism face. The prism and the grating are mounted in independent cells and are oriented so that the net deflection is minimized. In practice, the intense first order blaze wavelength is on axis and the weak zeroth order is at the edge of the field after diffraction. Following the grating, a 100 mm focal length positive achromat focuses the spectrum on a new focal plane that is coincident with the detector. | On the left, a 140 mm focal length negative achromat collimates the beam from the CDK telescope before it reaches the focal plane. At f/6.8 the beam for a point source on axis is 20.5 mm in diameter at this lens. Immediately after the lens the beam enters an anti-reflection coated wedge prism that deflects it 6 degrees off axis. This approximately compensates for the diffraction angle of a 150 groove/mm grating blazed at 580 nm that is close to the second prism face. The prism and the grating are mounted in independent cells and are oriented so that the net deflection is minimized. In practice, the intense first order blaze wavelength is on axis and the weak zeroth order is at the edge of the field after diffraction. Following the grating, a 100 mm focal length positive achromat focuses the spectrum on a new focal plane that is coincident with the detector. | ||
[[File:Grism_assembly_sm.jpg]] | |||
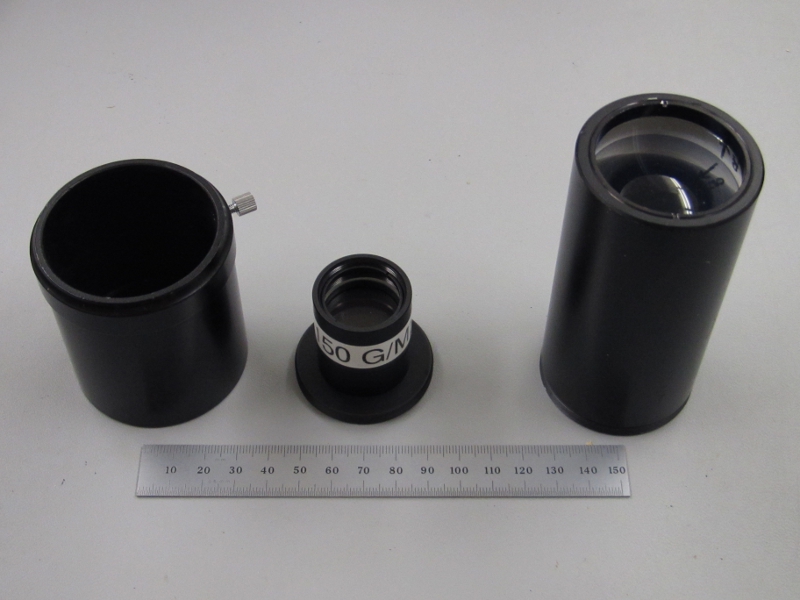
We assembled this device from a modified 2-inch Barlow lens assembly, adding Thorlabs holders for the prism, grating, and positive lens by mounting cells on an interior stop. This makes a compact rugged unit that inserts in the optical system between the telescope and the camera with minimal changes in the focal plane configuration. With a Manta G033B camera the spectra cover 4.8 A/pixel (0.48 nm/pixel) and span the visible spectrum. | We assembled this device from a modified 2-inch Barlow lens assembly, adding Thorlabs holders for the prism, grating, and positive lens by mounting cells on an interior stop. This makes a compact rugged unit that inserts in the optical system between the telescope and the camera with minimal changes in the focal plane configuration. With a Manta G033B camera the spectra cover 4.8 A/pixel (0.48 nm/pixel) and span the visible spectrum. | ||
Revision as of 01:37, 18 August 2011
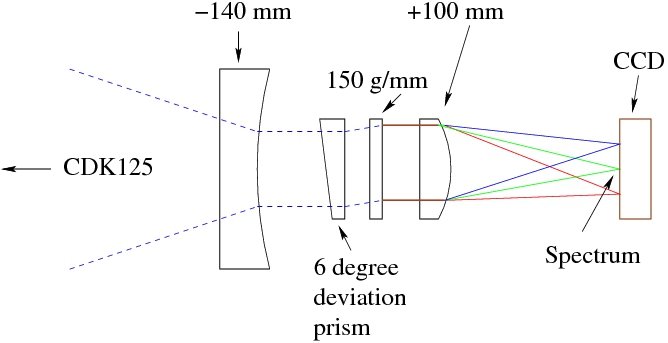
A combination of transmission diffraction grating and wedge prism (GRISM) may be placed in the optical path of a telescope to form an image of a spectrum. We have designed one for use with the CDK125 and one of the Manta CCD video cameras. A schematic of the optical system is shown below.
On the left, a 140 mm focal length negative achromat collimates the beam from the CDK telescope before it reaches the focal plane. At f/6.8 the beam for a point source on axis is 20.5 mm in diameter at this lens. Immediately after the lens the beam enters an anti-reflection coated wedge prism that deflects it 6 degrees off axis. This approximately compensates for the diffraction angle of a 150 groove/mm grating blazed at 580 nm that is close to the second prism face. The prism and the grating are mounted in independent cells and are oriented so that the net deflection is minimized. In practice, the intense first order blaze wavelength is on axis and the weak zeroth order is at the edge of the field after diffraction. Following the grating, a 100 mm focal length positive achromat focuses the spectrum on a new focal plane that is coincident with the detector.
We assembled this device from a modified 2-inch Barlow lens assembly, adding Thorlabs holders for the prism, grating, and positive lens by mounting cells on an interior stop. This makes a compact rugged unit that inserts in the optical system between the telescope and the camera with minimal changes in the focal plane configuration. With a Manta G033B camera the spectra cover 4.8 A/pixel (0.48 nm/pixel) and span the visible spectrum.